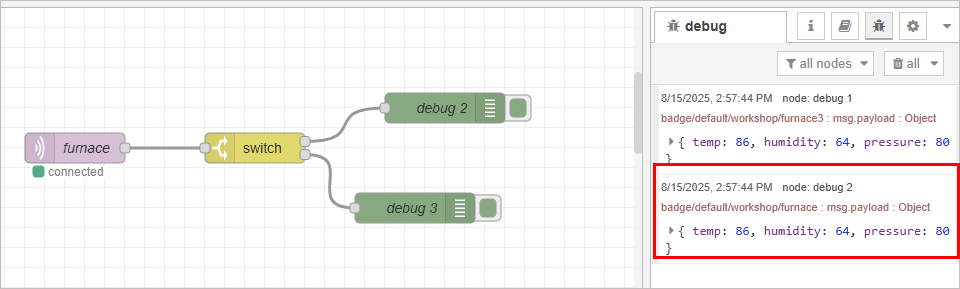
Example
The furnace data source contains 3 fields, and we want to route messages based on the temperature threshold:
- If temp > 85 → go to Output 1
- If temp ≤ 85 → go to Output 2
{
"furnace": {
"temp": 86,
"humidity": 64,
"pressure": 80
}
}
What Node to be Used?
In this example, we use the switch node to route messages according to conditions.

| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Property | The property path to evaluate. Commonly |
| Rules | A set of evaluation rules, each corresponding to one output port. |
| Type | The data type for comparison: number, string, boolean, JSONata, etc. info Ensures numeric comparisons are not treated as string comparisons. |
| Value | The value to compare against can come from: a constant value (e.g. 85),
|
| checking all rules | Evaluates all rules in order. If a message matches multiple rules, it will be sent to multiple outputs. |
| Stop after first match | Stops checking once the first rule matches, so the message is sent to only one output. |
| recreate message sequences | When enabled, preserves and rebuilds message sequence metadata (msg.parts)—usually created by a split node—so that the sequence is maintained even after branching. |
How to Filter Data?
- In Event Flow, add an mqtt in node to get the data from supOS.
- Drag in a switch node and configure its properties.
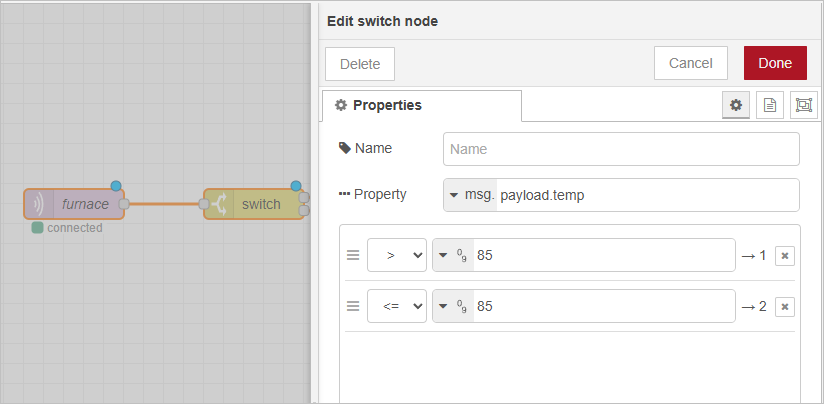
- Connect a debug node to each output of the switch node.
- Trigger the flow and check the results.